In this article, we connect a KY-023 Dual Axis Joystick Module to a Raspberry Pi Pico, any Rp2040 type board will be suitable. We actually tested this with a Cytron Maker Pi Pico
We will use Micropython for these examples but of course you can use the Arduino IDE as well if you have Raspberry Pi Pico support enabled
The KY-023 is an analog joystick sensor used for directional control in projects involving Arduino, Raspberry Pi, and other microcontrollers.
Overview
- Type: Analog Joystick Module
- Function: Measures position along two axes (X and Y) and includes a button for additional input.
- Applications:
- Game controllers
- Robotics
- RC vehicles and drones
- User interfaces and simulations
Key Features
- Dual-Axis Control: Measures movement along the X (horizontal) and Y (vertical) axes.
- Button Functionality: The joystick has a push-down switch when pressed.
- Spring Return: Automatically returns to the center position when released.
- Analog Output: Provides varying voltage signals based on the joystick’s position.
- Compatibility: Works with Arduino, Raspberry Pi, ESP32, and other microcontrollers.
Pinout and Connections
| Pin | Label | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground |
| 2 | +5V (VCC) | Power supply (3.3V to 5V) |
| 3 | VRx | Analog output for X-axis movement |
| 4 | VRy | Analog output for Y-axis movement |
| 5 | SW | Digital output for button (LOW when pressed) |
How It Works
- X-Axis (VRx): Provides analog voltage based on horizontal movement.
- Y-Axis (VRy): Provides analog voltage based on vertical movement.
- Button (SW): Acts as a digital switch that triggers when the joystick is pressed down.
- Center Position: When released, the joystick returns to the middle, with VRx and VRy reading around 2.5V (assuming 5V input).
- Edge Positions: Moving the joystick fully in any direction results in readings close to 0V or 5V.
Technical Specifications
| Feature | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V to 5V |
| Output Type | Analog (VRx, VRy), Digital (SW) |
| Button Type | Push-button (normally HIGH) |
| Axes Range | 0 to 1023 (10-bit ADC) |
| Module Size | 34mm x 26mm |
| Return to Center | Spring-loaded |
How to Interpret Output
- Neutral Position (Joystick Released):
- VRx and VRy will return values around 512 (2.5V) if using a 10-bit ADC (0-1023 scale).
- Full Left/Right (X-axis):
- Full left: ~0 (0V)
- Full right: ~1023 (5V)
- Full Up/Down (Y-axis):
- Full up: ~0 (0V)
- Full down: ~1023 (5V)
- Button:
- HIGH (1): Not pressed.
- LOW (0): Pressed.
Applications
- Game Controllers: Use for directional control in custom gamepads.
- Robotics: Control movement or arm positioning.
- RC Projects: Control motors, servos, or speed controllers.
- User Interfaces: Use as a general input device for menu navigation.
- Camera Gimbals: Position and pan cameras using the joystick.
Parts Required
You can connect to the module using dupont style jumper wire.
| Name | Links |
| Raspberry Pi Pico | |
| 37 in one sensor kit | |
| Connecting cables |
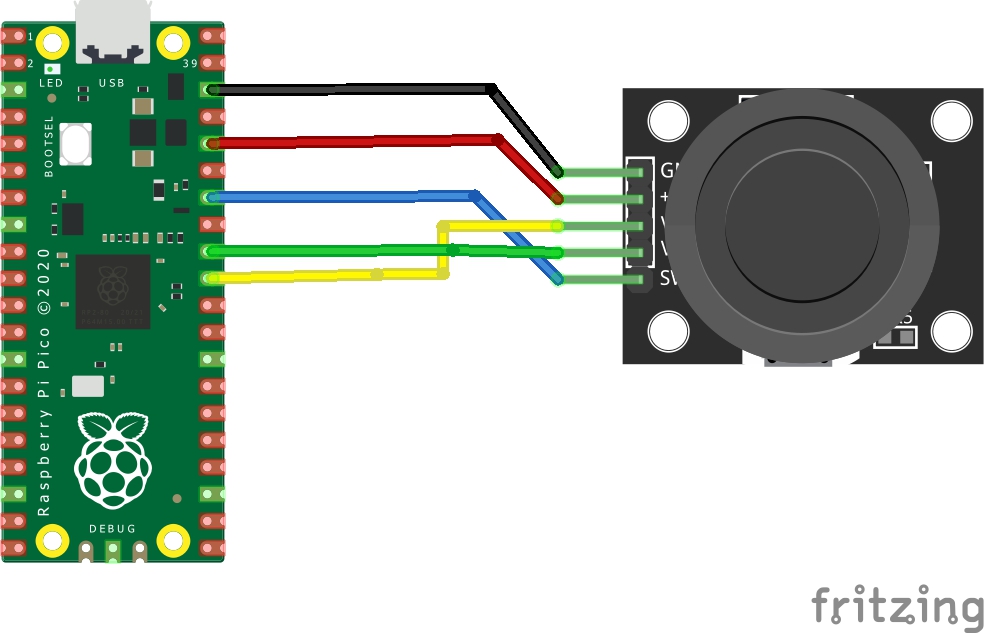
Schematic/Connection
| Pico | Sensor |
|---|---|
| GND | GND |
| 3 V | +V |
| GPIO26 | VRx |
| GPIO27 | VRy |
| GPIO28 | SW |
Code Examples
from machine import Pin, ADC
import utime
# Initialization of pins
SW = Pin(28,Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP)
VRx = ADC(0)
VRy = ADC(1)
# Endless loop for reading the joystick and switch
while True:
# Read the analog values and convert to voltage
xAxis = round(VRx.read_u16() * 3.3 / 65536, 2)
yAxis = round(VRy.read_u16() * 3.3 / 65536, 2)
# read the value
switch = SW.value()
# Serial output of the received values
print("X-axis: " + str(xAxis) + ", Y-axis: " + str(yAxis) + ", Button: " + str(not(switch)))
utime.sleep_ms(500)
REPL Output
Disclaimer
This website may contain affiliate links, which means we may receive a commission if you click on a link and make a purchase. This comes at no additional cost to you.